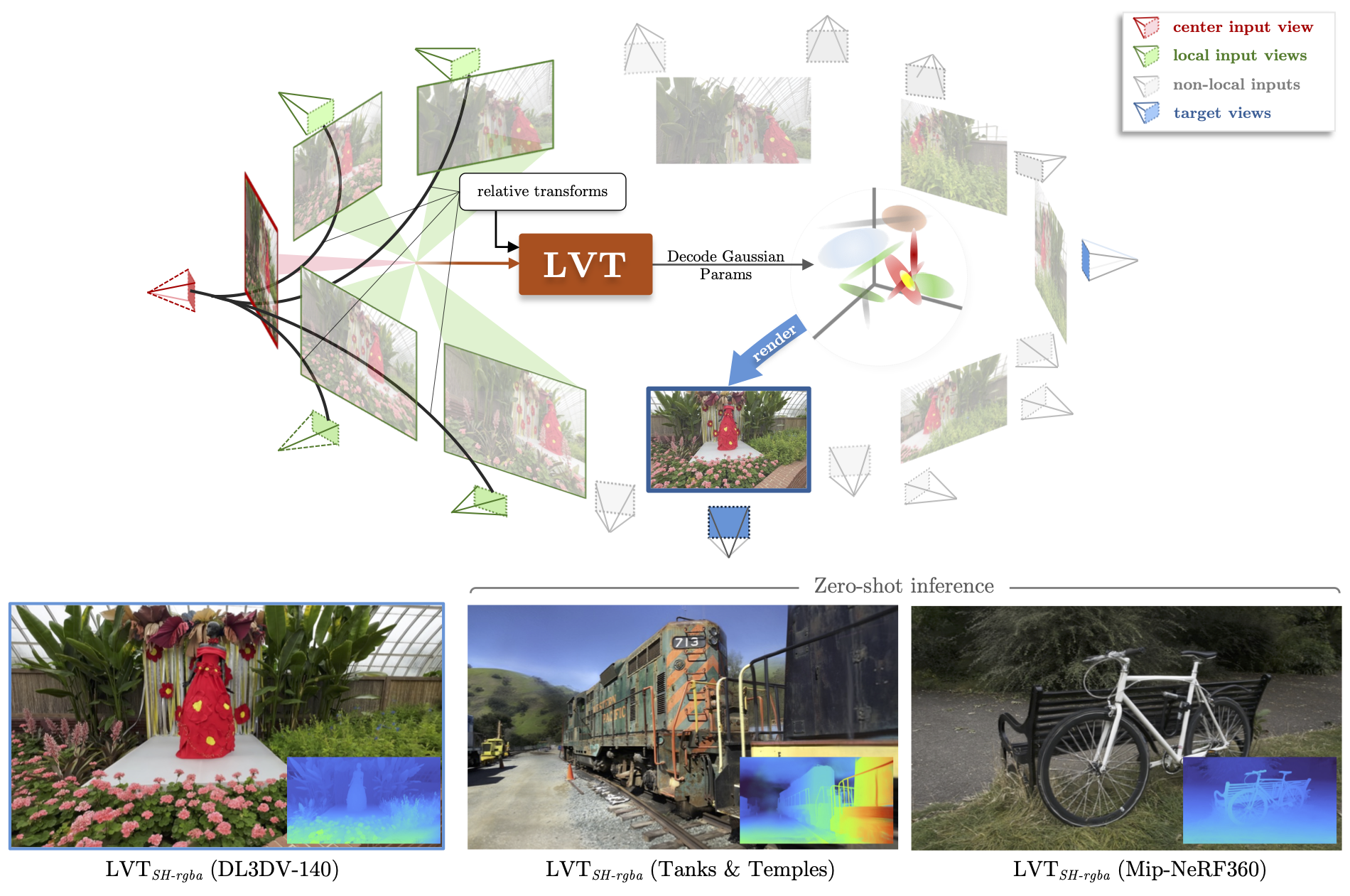
LVT: Large-Scale Scene Reconstruction via Local View Transformers
ACM SIGGRAPH Asia 2025
LVT enables efficient reconstruction of large, high-resolution scenes in a single forward pass. By leveraging a linear-complexity neighborhood attention mechanism, conditioning on relative camera poses, and incorporating view-dependent opacity, we achieve state-of-the-art results across diverse datasets and variable sequence lengths.
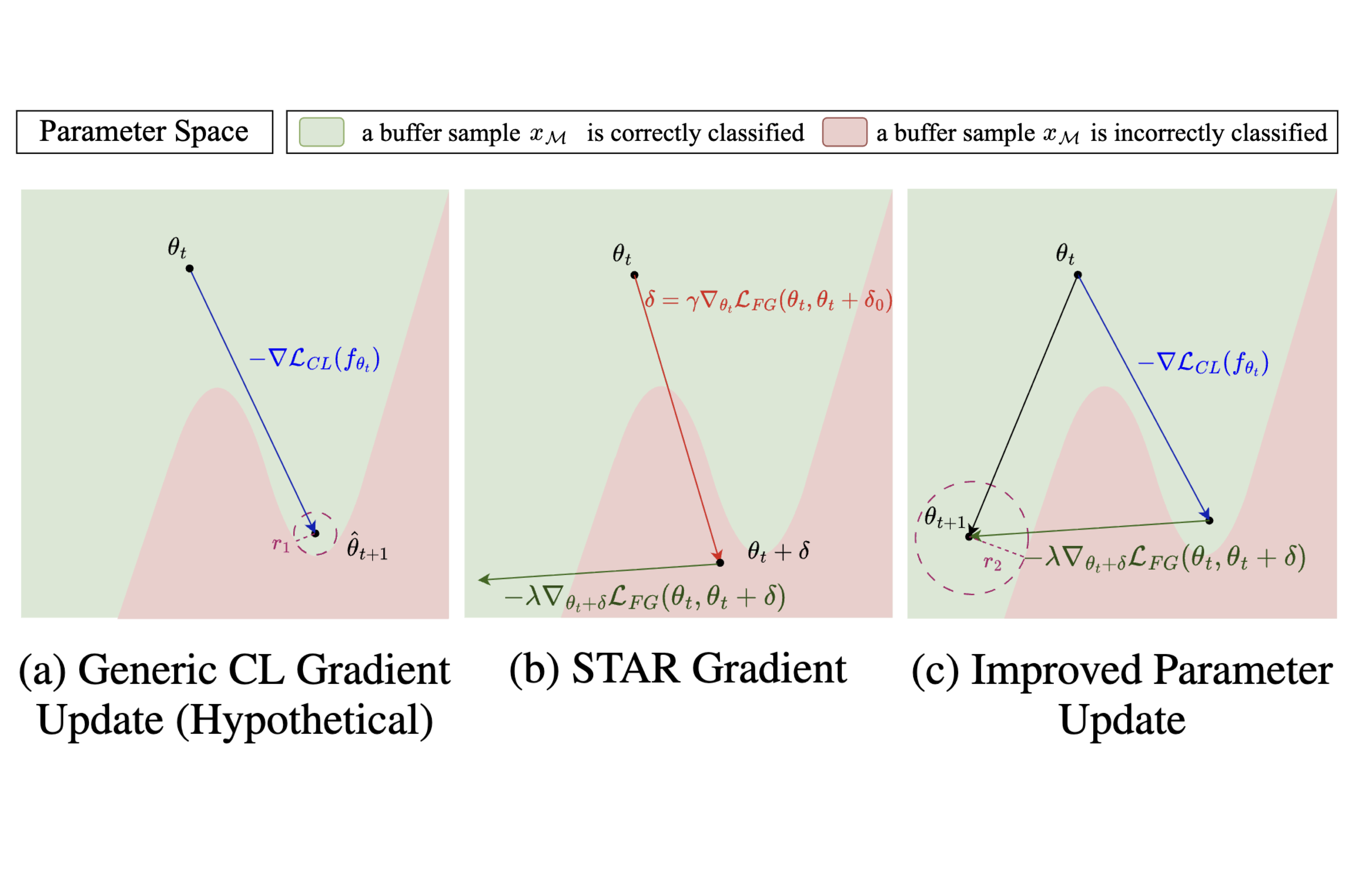
STAR: Stability-Inducing Weight Perturbation for Continual Learning
International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR) 2025
In continual learning models, STAR exploits the worst-case parameter perturbation that reduces the KL-divergence of model predictions with that of its local parameter neighborhood to promote stability and alleviate forgetting. Empirically, STAR, which can be integrated as a plug-and-play component, consistently improves performance of existing rehearsal-based CL methods by up to 15% across several baselines.
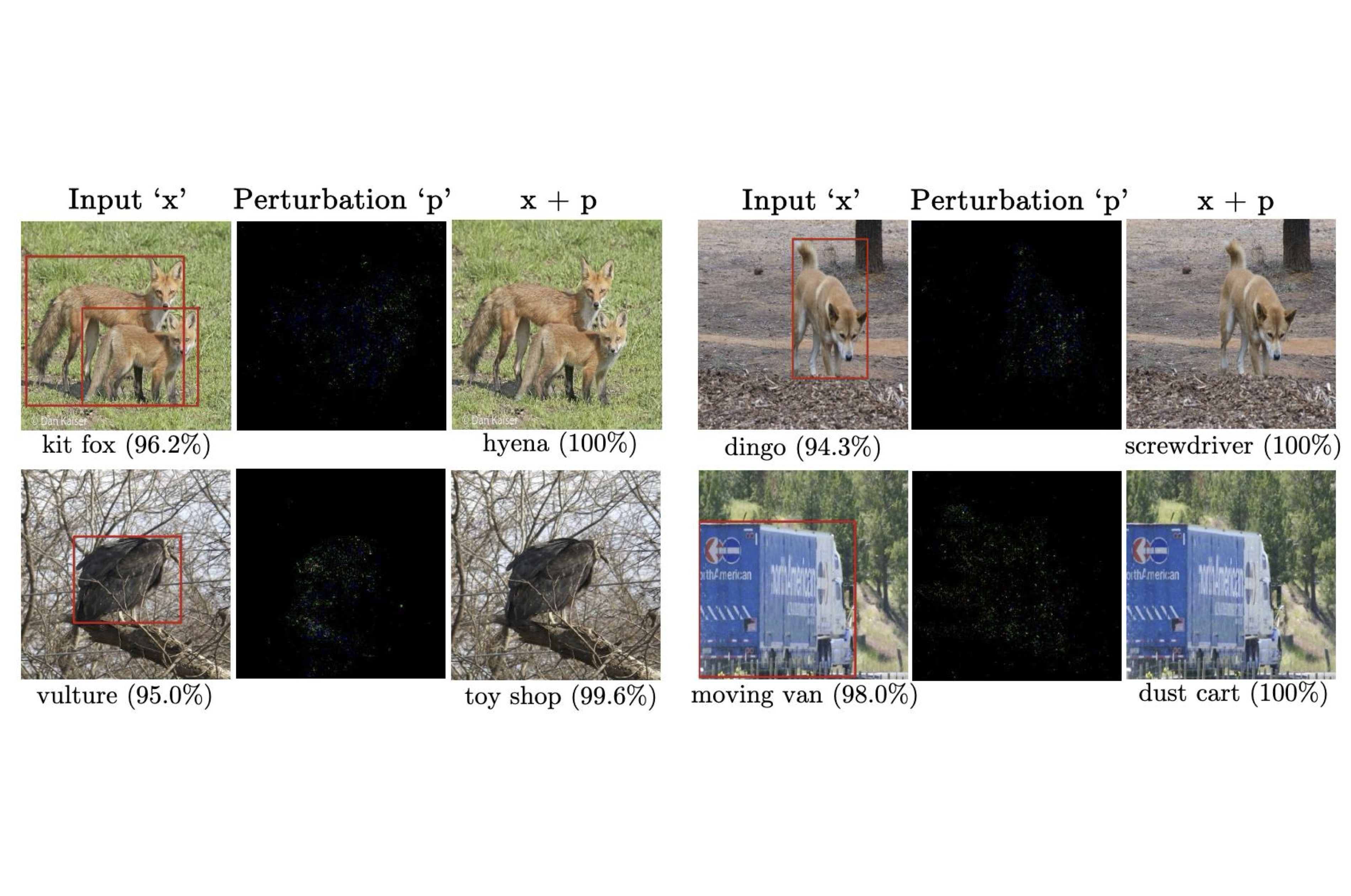
SAIF: Sparse Adversarial and Imperceptible Attack Framework
Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR), 2025
We design imperceptible attacks that contain low-magnitude perturbations at a few pixels, and leverage these sparse attacks to reveal the vulnerability of classifiers. We use the Frank-Wolfe algorithm to simultaneously optimize the attack perturbations for bounded magnitude and sparsity with O(1/√T) convergence. Empirically, SAIF computes highly imperceptible and interpretable adversarial examples, and largely outperforms state-of-the-art sparse attack methods on ImageNet and CIFAR-10.
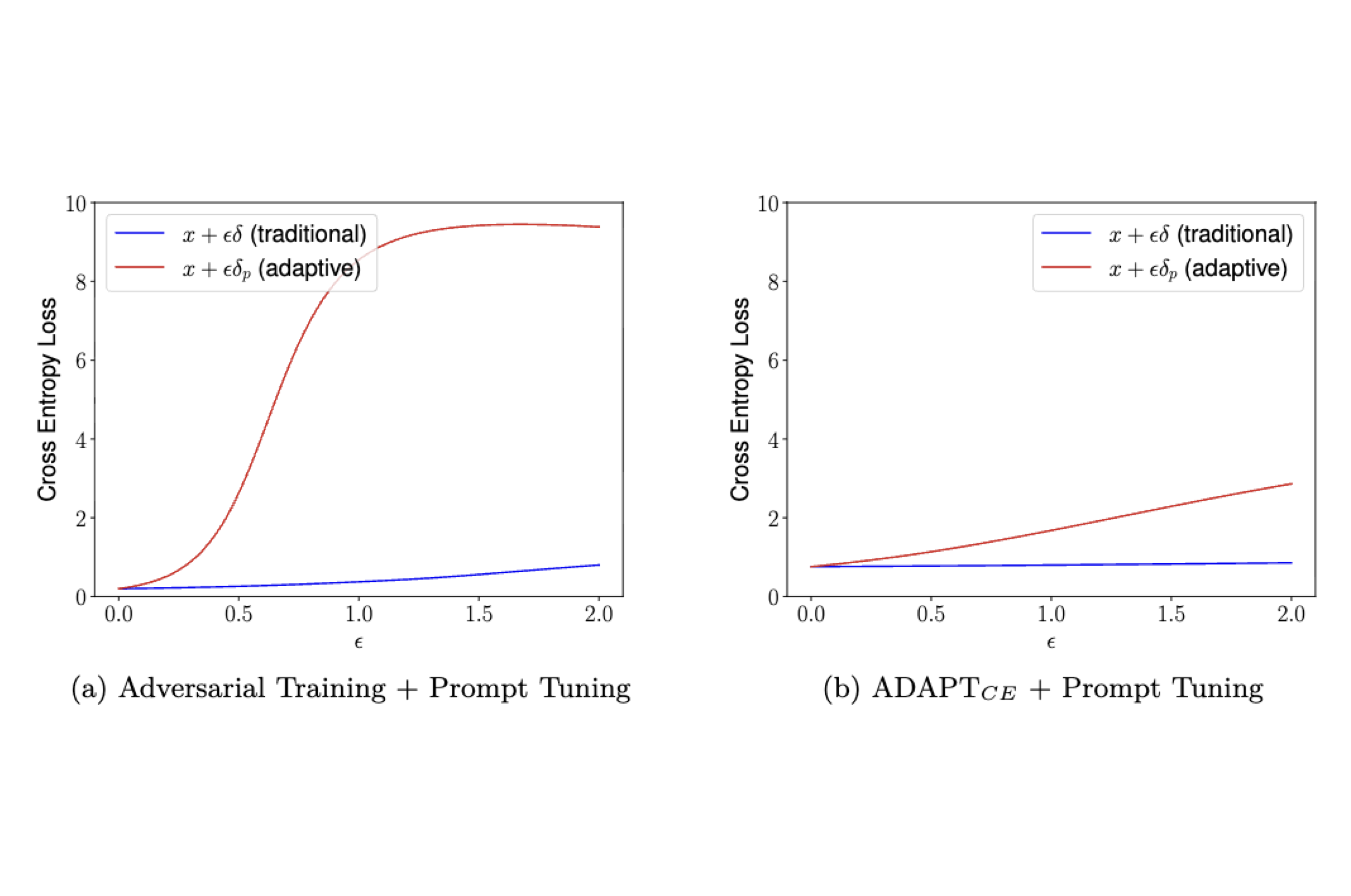
ADAPT to Robustify Prompt Tuning Vision Transformers
Transactions on Machine Learning Research (TMLR), 2025
ADAPT is a novel framework for performing adaptive adversarial training in the prompt tuning paradigm. It achieves competitive robust accuracy of ∼40% w.r.t. SOTA robustness methods using full-model fine-tuning, by tuning only ~1% of the number of parameters.
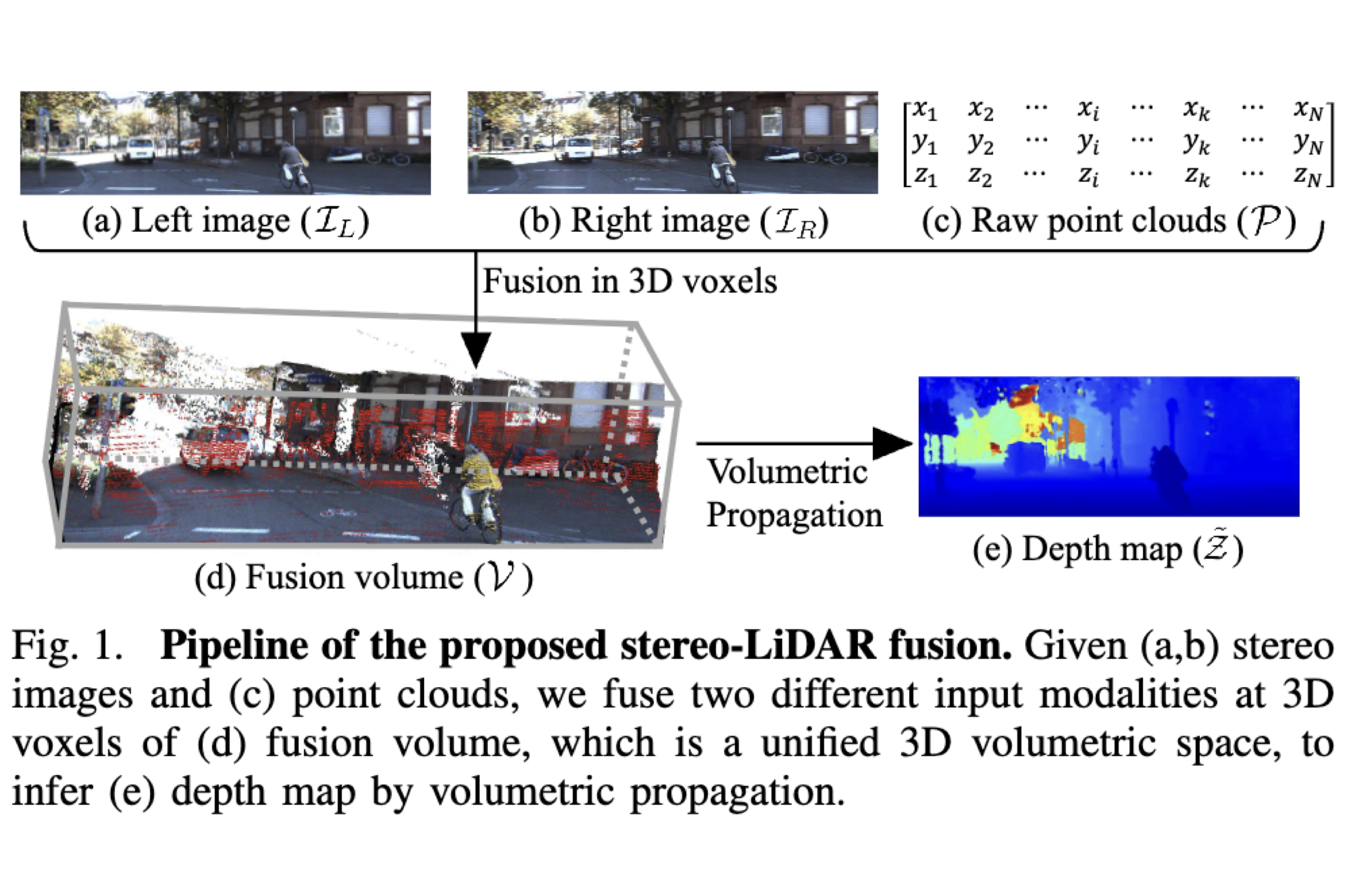
Volumetric Propagation Network: Stereo-LiDAR Fusion for Long-Range Depth Estimation
IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021
VPN is a geometry-aware stereo-LiDAR fusion network for long-range depth estimation. It exploits sparse and accurate point clouds as a cue for guiding correspondences of stereo images in a unified 3D volume space. It achieves state-of-the-art performance on the KITTI and the VirtualKITTI datasets among recent stereo-LiDAR fusion methods.
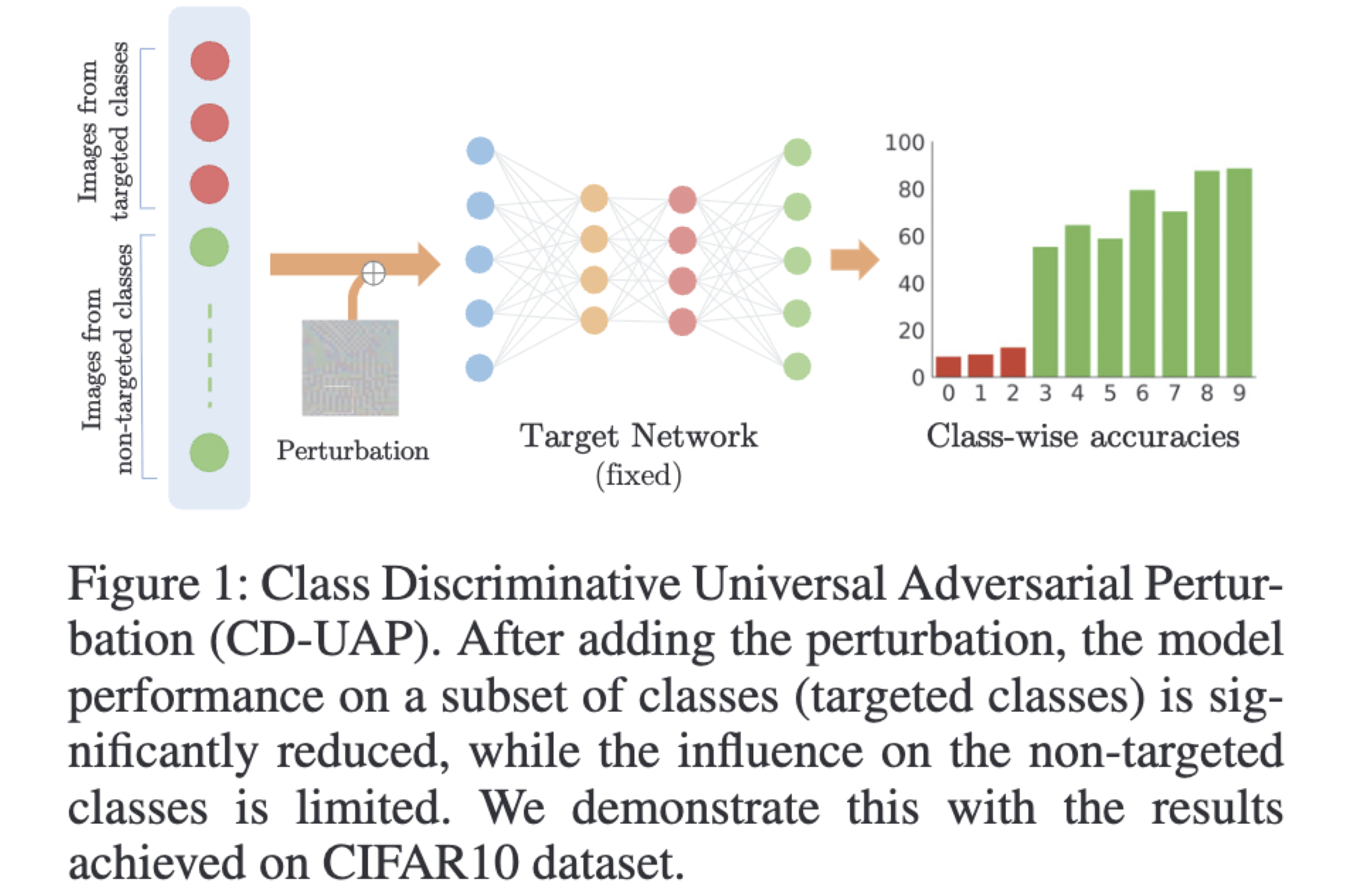
CD-UAP: Class Discriminative Universal Adversarial Perturbation
Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020
We propose a new universal attack method to generate a single perturbation that fools a target network to misclassify only a chosen group of classes, while having limited influence on the remaining classes. Beyond class-discriminative UAPs, CD-UAP also achieves state-of-the-art performance for the original task of UAP attacking all classes.
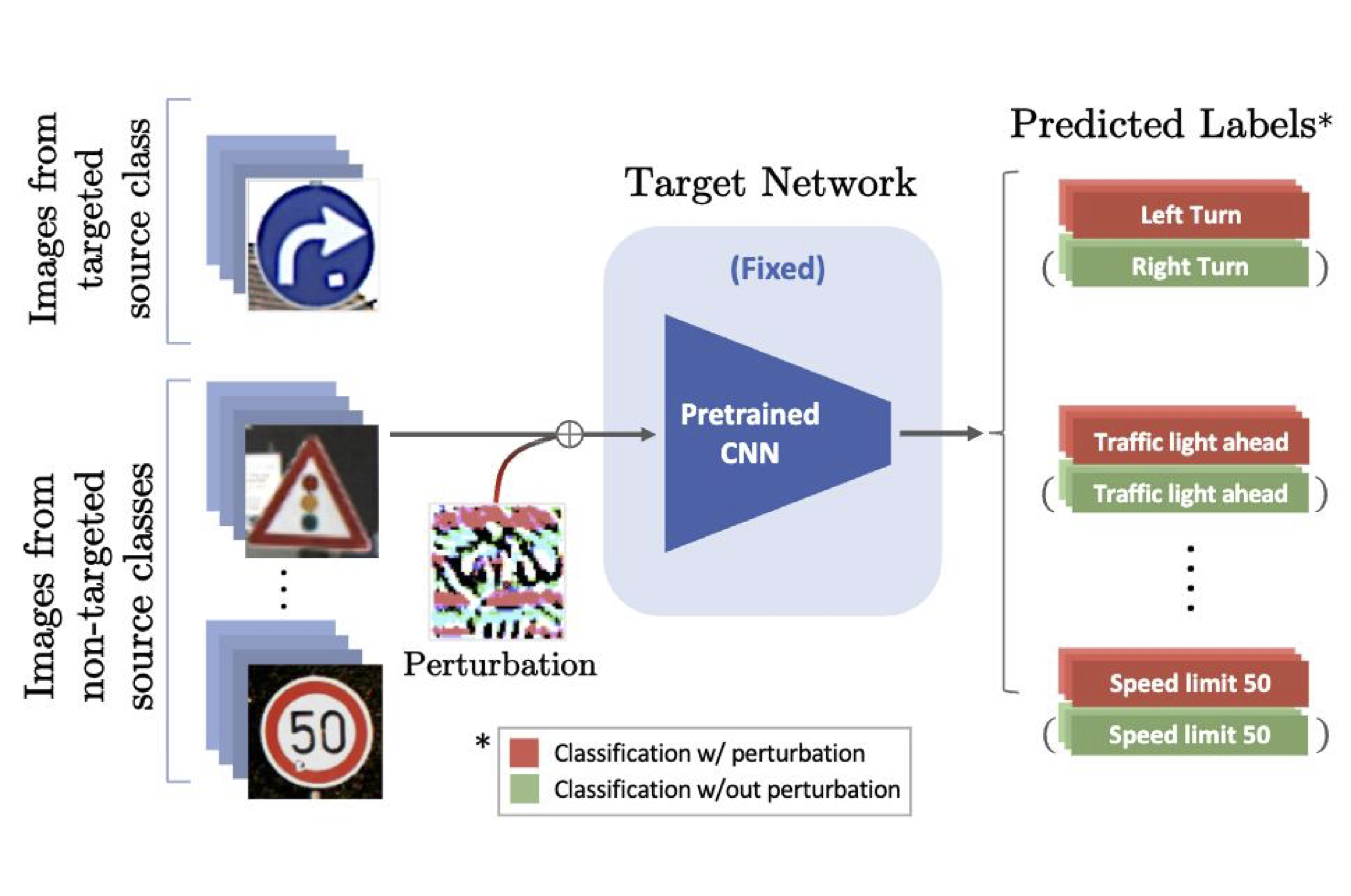
Double Targeted Universal Adversarial Perturbations
Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision, 2020
DT-UAPs attack one targeted source class to sink class, while having a limited adversarial effect on nontargeted source classes. Targeting the source and sink class simultaneously, we term it double targeted attack (DTA). This provides an attacker with the freedom to perform precise attacks on a DNN model while raising little suspicion. We show the effectiveness of the proposed DTA algorithm on various datasets and also show its potential as a physical attack.
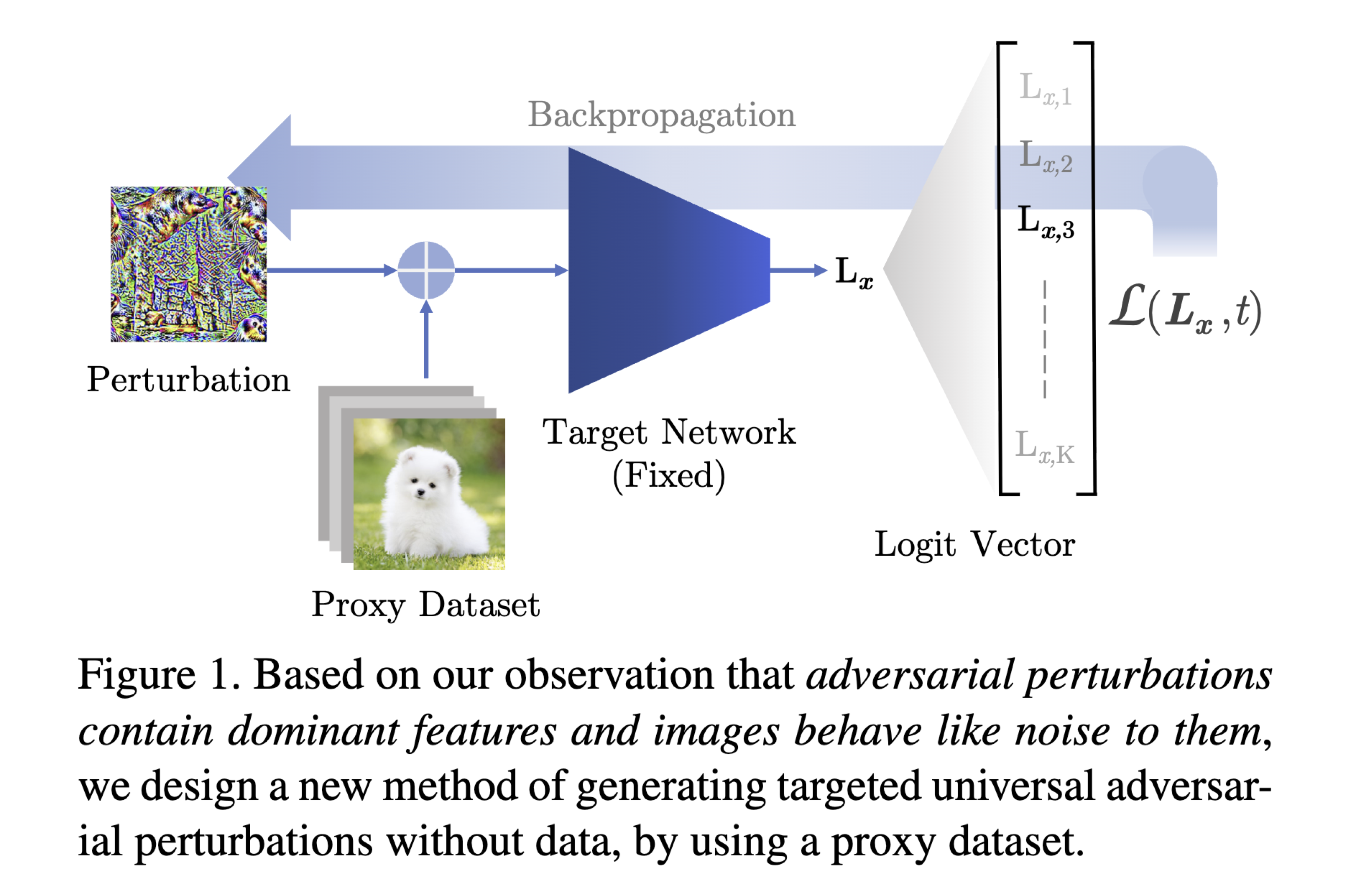
Understanding Adversarial Examples From the Mutual Influence of Images and Perturbations
Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020
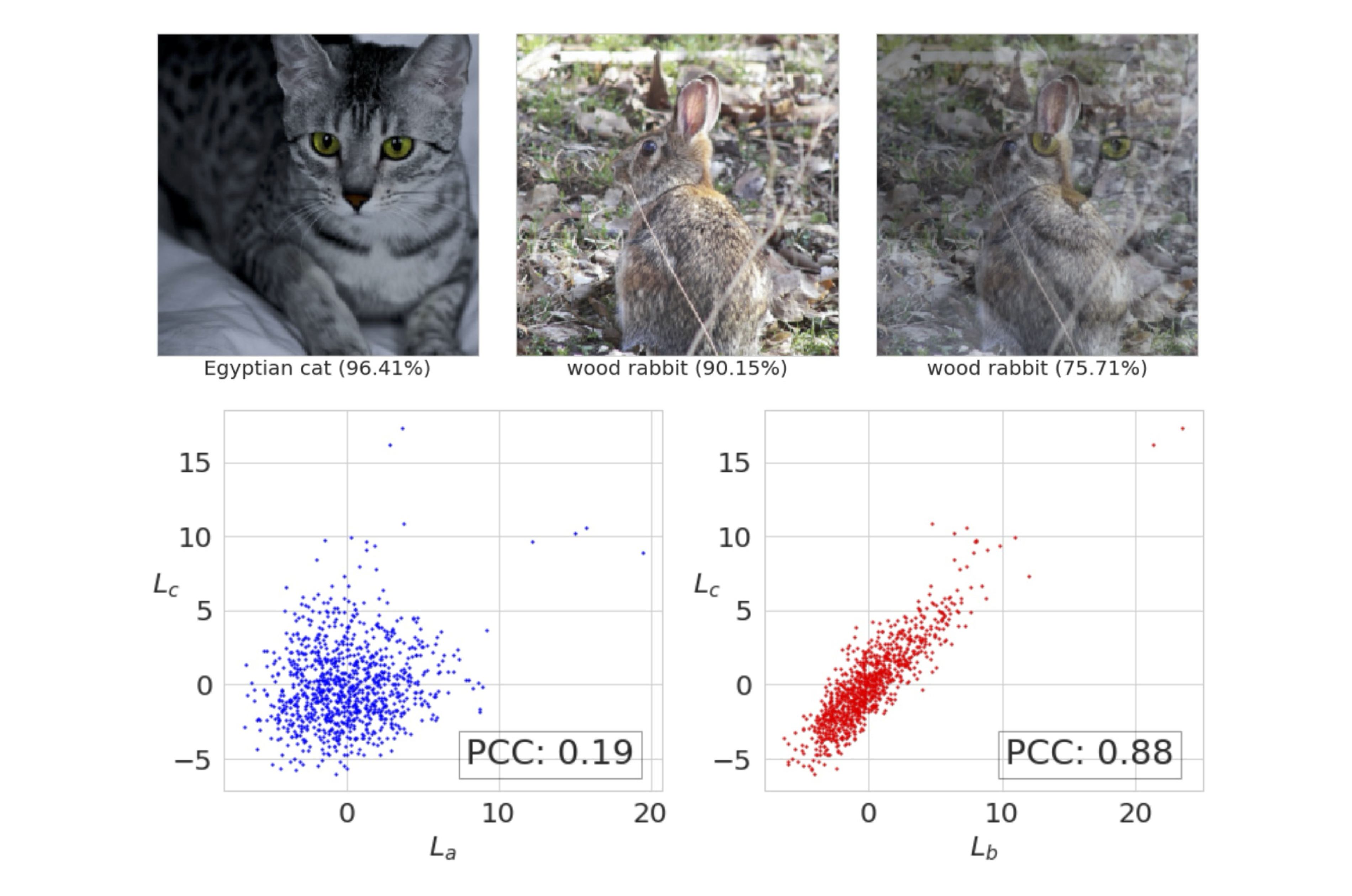
We treat DNN logits as feature vectors and use the Pearson correlation coefficient to analyze the mutual influence between independent inputs, enabling a disentangled analysis of clean images and adversarial perturbations. This analysis reveals that universal perturbations contain dominant features while images behave like noise, motivating a new method for generating targeted UAPs from random images. Our approach is the first to achieve targeted universal attacks without access to original training data and performs comparably against state-of-the-art methods using only a proxy dataset.
Data from Model: Extracting Data from Non-robust and Robust Models
CVPR 2020 Workshop on Adversarial Machine Learning in Computer Vision

Universal Adversarial Perturbations are Not Bugs, They are Features
CVPR 2020 Workshop on Adversarial Machine Learning in Computer Vision